EN3262 Postcolonial/Postmodern Writing

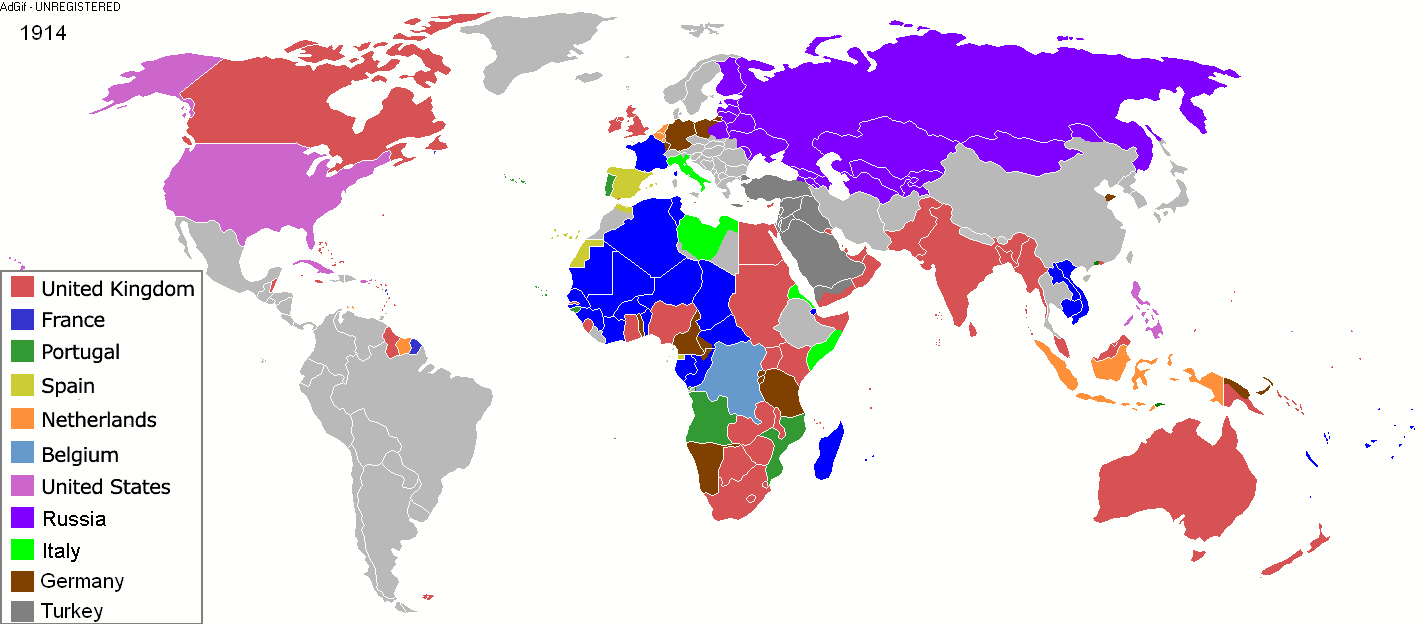
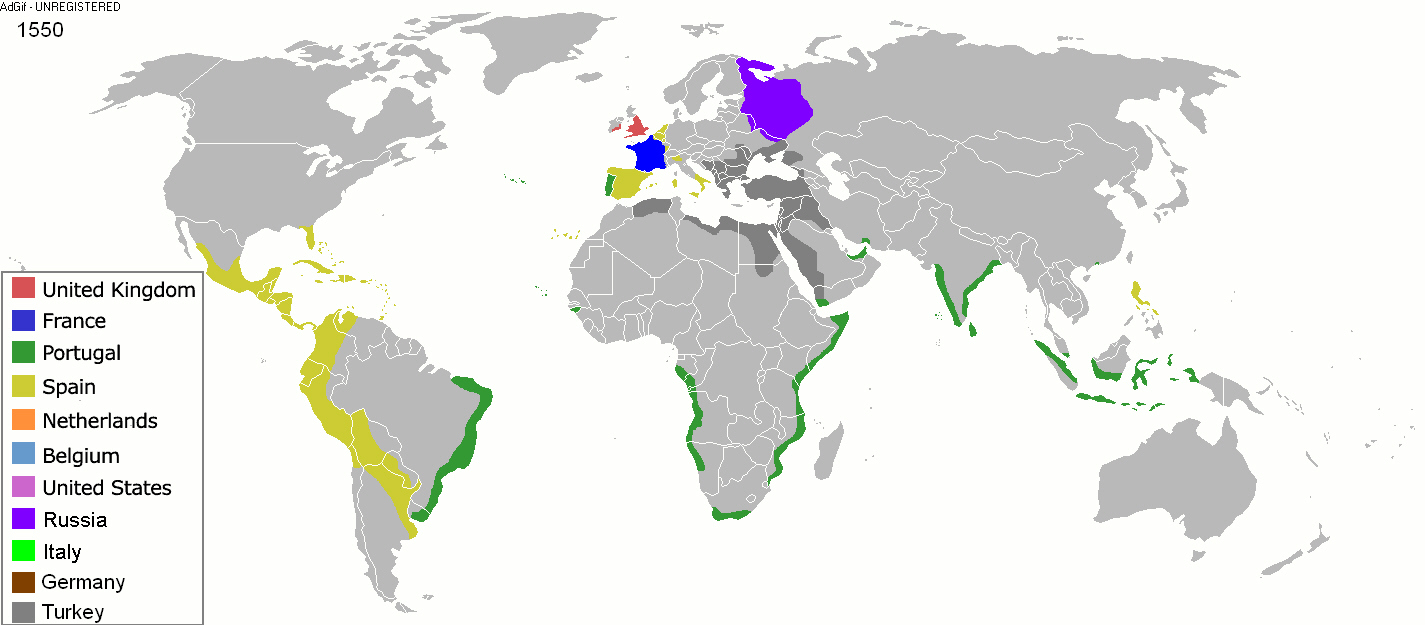
[Source: Wikipedia]
Imperialism in modern history
The term imperialism, "the
policy and practice of forming and maintaining an empire," usually refers
to the great overseas empires of Europe during the past five hundred years.
Imperialism involved:
1 The systematic and organized domination of peoples and nations by a
single nation, brought about through
2 Territorial annexation or conquest, and
3 Economic control and exploitation
Motives for territorial
expansionism:
1
Economic
2
Strategic
3 Colonizing
Factors enabling
Imperialism/Colonization:
1 Technological superiority: navigation, guns, etc.
2 Organizational skills
3 Highly developed sense of national interest
4 Highly developed trading skills
5 Aggressive self-interest
Disabling Factors for the
colonized:
1 Poor technology
2 Poor organization
3 Poor sense of national self-interest
4 Naive trading practices
5 Confused, self-divisive motives
Consequences of colonization for
the colonizer:
1
Wealth & power
2
Territory
3
Sense of national superiority/destiny/role in world history
4 Sources of raw materials for its trade and industries
5 Markets for its trade and industries
Consequences of colonization for
the colonized:
1
Depletion of wealth and resources
2
Retarded political, economic, and social development
3
Habits of dependency
4
Lack of self-identity and self-confidence
5
Deracination or confused cultural identity
6
`Orientalization'
Positive: Modernization
1 Access to colonizer's language/culture/system of education
2 Access to colonizer's technology and expanded trade options
3 Access to colonizer's institutions of government, law, organization, etc.
[Last Updated: 10 August 2010]